Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Cognitive method of life and disease of traditional Chinese medicine, one of traditional Chinese medicine, is declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine and one of the national intangible cultural heritages.
The recognition of life and disease in traditional Chinese medicine is a kind of medical knowledge based on the understanding of human life phenomena and disease laws produced by traditional Chinese culture. The knowledge of life and disease in TCM mainly includes Yin and Yang, Five Elements, viscera, meridians, diseases and syndromes, etiology and pathogenesis, differentiation of symptoms and signs, treatment principles and methods, five elements and six qi.
On May 20, 2006, the cognitive methods of life and disease in traditional Chinese medicine were listed in the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage list of traditional medicine, item number IX-1.
historical origin
The knowledge of life and disease in traditional Chinese medicine originated from the legendary ancient Huangdi and Qibo times, marked by the Yellow Emperor's Internal Classic. Its knowledge system has been formed for more than two decades.
The Yellow Emperor's Internal Classic puts forward the view of disease that "righteousness exists inside, evil cannot be done", "where evil is gathered together, its Qi must be deficient".
Zhang Zhongjing's Treatise on Febrile Diseases and Miscellaneous Diseases in the Eastern Han Dynasty and other early documents recorded a large number of knowledge about diseases.
In the Sui Dynasty, there are 67 phylums and 1720 kinds of diseases and syndromes recorded in the treatise on the origins and symptoms of various diseases.
In modern times, influenced by Western medicine, the number of people who can understand and inherit the knowledge of life and disease of traditional Chinese medicine is decreasing, and they are facing the dilemma of preservation and development.
Non-legacy features
The knowledge of life and disease in TCM mainly includes Yin and Yang, five elements, viscera, meridians, etiology and pathogenesis, differentiation of symptoms and signs, treatment principles and methods, five elements and six qi.
Yin and Yang
Traditional Chinese medicine uses the concept of the unity of opposites between Yin and Yang to elaborate human life activities and the interdependence between human beings and the external environment such as nature and society. The balance between yin and Yang is the basis of maintaining and guaranteeing human life activities, and the imbalance between yin and Yang leads to the change of diseases.
Five elements
Traditional Chinese medicine uses the theory of five elements to elaborate the relationship between human body and nature, the various parts of the human body and the mechanism of disease occurrence and development, and to guide the treatment of diseases.
- Visceral elephants
Visceral image is an important life phenomenon of human body. It mainly includes five viscera, six viscera, odd and constant viscera, physiological function and pathological changes of essence, qi, blood and body fluid.
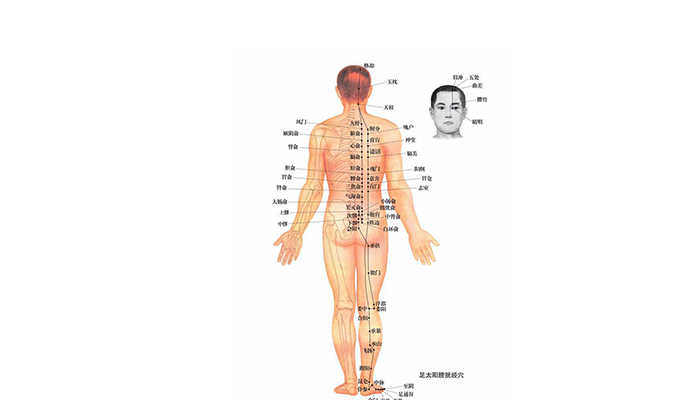
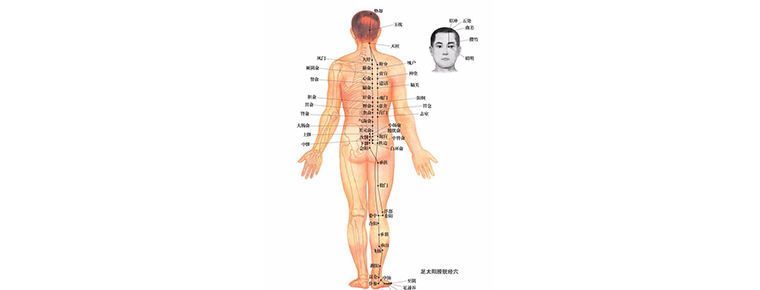
Channels and collaterals
Meridians and collaterals are channels for the movement of Qi and blood, and they have the function of connecting the whole body. Meridian system, including twelve meridians, eight odd meridians and collaterals, is the basis of the diagnosis and treatment of diseases in traditional Chinese medicine, as well as the important theoretical basis of acupuncture, massage and other therapies.
- Etiology and pathogenesis
The etiology is the theory of studying the causes and conditions of diseases, including exogenous six pornography, internal injury seven emotions and dietary fatigue. Pathogenesis theory is a theory that studies the law of disease occurrence and development.
Syndrome differentiation
Differentiation of symptoms and signs is to use the methods of seeing, hearing, asking and cutting to diagnose diseases, to analyze and synthesize the results of diagnosis and to draw conclusions, and to establish the principles of treatment.
Rule of law
Therapeutic principles and methods are the basic principles and methods that must be followed in the treatment of diseases. They are the treatment rules summarized in the long-term clinical practice of TCM. They mainly include adjusting Yin and Yang, strengthening the right and dispelling pathogens, prioritizing specimen, and adjusting measures according to people, time and local conditions.
Five lucks and six lucks
The five elements and six elements are systematic knowledge for studying and exploring the effects of astronomical, meteorological and phenological changes on human health and diseases.
Inheritance and Protection
Inheritance value
Chinese traditional medicine regards "the cognitive method of life and disease of traditional Chinese medicine" as an important content, expands and deepens the connotation of "non-legacy". It can best embody the spirit and soul of "non-legacy". It is the general outline of intangible cultural heritage of traditional medicine.
Cognition of life and disease in TCM is the core of TCM knowledge. It plays a guiding role in various aspects of TCM health preservation, diagnosis, treatment, prescription, traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture and moxibustion and clinical practice.
Heritage figures
Lu Zhizheng, male, was born in December 1920. In June 2007, Lu Zhizheng was selected as the representative successor of the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage projects, declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Project Name: Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Wang Mianzhi, male, was born in November 1923. In June 2007, Wang Mianzhi was selected as the representative successor of the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage projects, declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Project Name: Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Yan Dexin, male, was born in November 1920. In June 2007, Yan Dexin was selected as the representative successor of the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage projects and declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Project Name: Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Cao Hongxin, male, was born in February 1958. In June 2007, Cao Hongxin was selected as the representative successor of the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage projects and declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Project Name: Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Wu Xianzhong, male, was born in August 1925. In June 2007, Wu Xianzhong was selected as the representative successor of the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage projects and declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Project Name: Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Chen Keji, male, was born in October 1930. In June 2007, Chen Keji was selected as the representative successor of the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage projects and declared by the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Project Name: Cognitive Method of Life and Disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
protective measures
On May 20, 2006, the cognitive method of life and disease of TCM was approved by the State Council and listed in the first batch of national intangible cultural heritage list.
social influence
Important activities
On July 15, 2012, with the approval of the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China and the National Natural Science Foundation Committee, the opening ceremony of the National Graduate Summer School of Life and Disease Cognition of Chinese Medicine in 2012, sponsored by the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, was held in Beijing.
-
1.Serdang snow mountain Xiling snow mountain
Xiling Snow Mountain, located in Dayi County, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, is only 95 kilometers away from Chengdu, with a total area of 483 square kilometers. It is a world natural heritage
Time 2018-10-30 -
2.Terracotta Army
Terracotta Warriors and Horses, terracotta warriors and horses of Qin Shihuang, also referred to as terracotta warriors and horses or terracotta warriors and horses of Qin Dynasty
Time 2018-11-11 -
3.Online Shopping
Online shopping is to retrieve commodity information through the Internet, and send out shopping requests through electronic order forms, then fill in the number
Time 2018-11-13 -
4.Yesanpo Scenic Area Laishui County Baoding
The Yesanpo Scenic Area of Laishui County, Baoding City, Hebei Province, is located in Laishui County, Baoding City. The Taihang Mountains and Yanshan Mountains
Time 2018-11-24 -
5.Privacy Policy
We takes users' information safety and privacy as our lifeline. Based on our basic principle "Users' needs are our first priority", we are committed to enhancing the transparency of informat
Time 2018-12-08 -
6.Chengji Mountain Tourist Scenic Spot
Qiu Mountain, also known as Linglong Mountain, Xianshan Mountain on a journey to the West and Qiu Mountain Scenic Area, is located in Suiping County, Zhumadian City, Henan Province
Time 2018-12-09 -
7.Anguo City
Anguo City, formerly known as Qizhou, is now the jurisdiction area of Baoding City, Hebei Province, 100 kilometers south of Shijiazhuang, the provincial capital.
Time 2019-03-30 -
8.Two tones of Han tune
Originally known as "Shan Er-huang", "Tu Er-huang" or "Shan Er-huang", the second largest traditional opera in Shaanxi Province is one of the traditional local operas in
Time 2019-05-02 -
9.Nuuziz Festival
The word "Nuruzi" comes from the ancient Iranian language and means "spring rainy day". On March 21 of each year, like the Spring Equinox, it means the arrival of spring. Uygur, Ta
Time 2019-06-08 -
10.Uygur Costume
Uygur costumes - more patterns, very beautiful, full of characteristics. Uygur men - pay attention to black and white effect, so bold and unrestrained. Uygur women prefer to use contrasting colors to
Time 2019-06-26 -
11.Xie Rong Zhongzi
Xierong Zhongzi still keeps the primitive and simple legacy, from which we can see the spiritual sustenance and aesthetic pursuit of Tibetan ancestors. This kind of primitive culture and art has becom
Time 2019-07-06 -
12.Nanchong first industry
In 2019, the sown area of grain crops in Nanchong is 558000 ha, which is 0.15% lower than that in 2018. The sown area of oil crops is 152000 ha, an increase of 1.9% over that in 2018. The vegetable planting area is 154000 hectares, an increase of 3.9% over that in 2018.
Time 2020-12-17